Using the Triage Assessment Form
Using the Triage Assessment Form Jordan is a married female that is in fear of not just her safety, but…
Occupational Therapy Programs for ADD/ADHD & Dyslexia
Children diagnosed with ADD, ADHD or dyslexia commonly have learning disorders or problems achieving their best. Youngsters having attention deficit…
ADHD Symptoms in a Baby
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is usually diagnosed when a child reaches school age. Although doctors are reluctant to give…
Behavior Management Techniques for ADHD Kids
If your child has Attention Deficit with Hyperactivity Disorder, you are well aware of the obstacles he faces every day.…
Appropriate Goals for Children with Behavioral Problems
Children with behavioral problems can be a challenge for parents, teachers and even their own peers. Kids need boundaries and…
Psychological effects of epilepsy on children
Epilepsy is a disease that affects the nervous system. Around 750,000 children were diagnosed with epilepsy in the United States…
Psychological effects of diabetes on children
When most people think of diabetes, they think of an overweight adult who has caused the majority of their own…
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
1. Provide an introduction (Please answer the following questions in your answer: State the relevance to social work and how…
A Comparison of Maternal and Paternal Filicide
Abstract This study intends to explore the differences between maternal and paternal filicide. The sample population consists of five males…
How much does a circumcision cost?
Like any medical procedure, the cost of circumcision varies from one provider to the next and one state or region…
Is the salary of a Speech Language Pathologist worth the amount of school?
So you’ve decided being a Speech and Language Pathologist might be the career calling you’re been waiting for. Now you’re…
Activities to Build Self Esteem in Adolescents
As if the physical changes and hormonal fluctuations of adolescence are not enough to put youngsters in an emotional and…
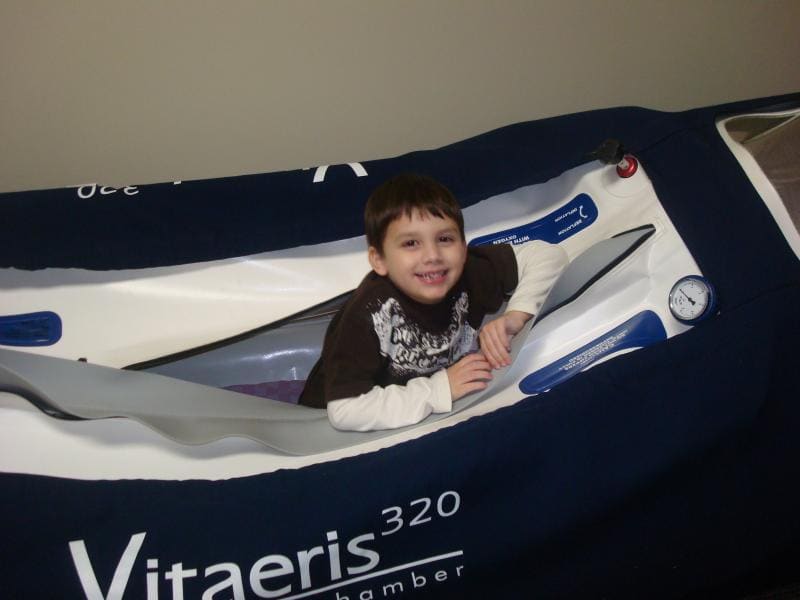
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Side Effects
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy or HBOT involves lying on a table within an enclosed chamber, which contains predetermined levels of pure…
Spot Autism Symptoms In Teenagers
As children with autism evolve into teenagers, they are confronted with a new set of challenges that can cause the…
Why Is Cognitive Development Important In Preschool?
From the time your child is conceived until they finish elementary school, the concept of cognitive development is a hot…
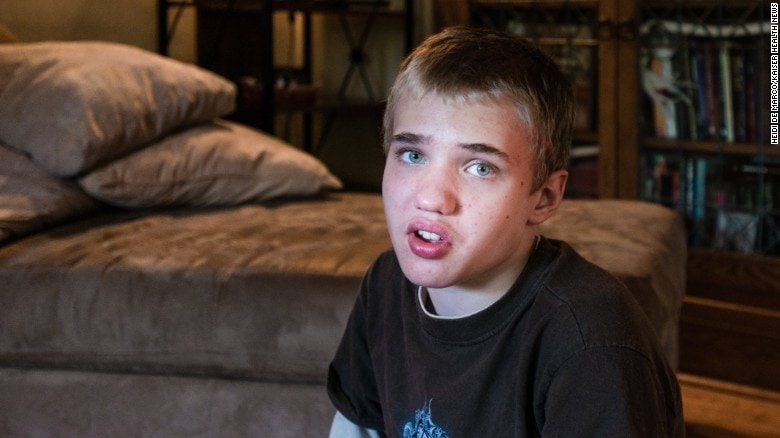
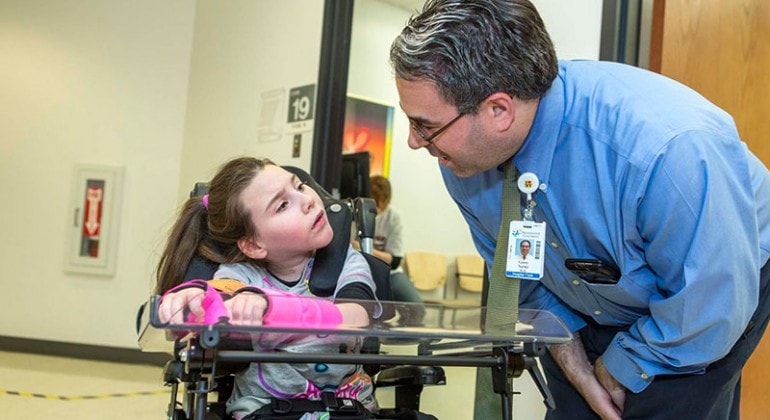
The Social, Emotional, & Psychological Effects Of Adults With Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a cluster of brain disorders that affect an individual’s ability to move, balance, and control posture,…
Different Ways that Adolescents Take Oxycodone
According to statistics, in 2014, more than 460,000 adolescents admitted to abusing prescription pain relieving medications. More than half of…
What Are The Benefits Of Behavioral Theories?
Behavioral theories are used to predict the way that a person or group of people will react to a certain…
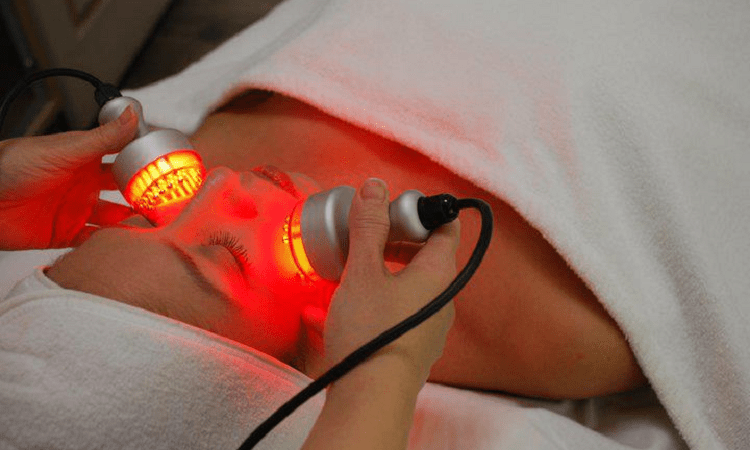
Red Light Therapy for Acne
When it comes to acne treatment, there are a number of different methods that you can use to try and…
Psychological Impact Of Puberty
Many a parent witnesses a sweet, innocent and loving child seemingly transform overnight once puberty begins. Despite the talks provided…